Technology Licensing
Technology Licensing Procedure
Types of Technology Licensing
Definition of Technology Licensing
Technology Licensing refers to the act of providing full execution rights to or acceding all rights due to the request of the inventor of the technology (intangible products such as patent rights, program, know-how etc.), request of a corporation with demand for the technology, or TLO marketing.
Technology Consultation
▶ Receiving expert consultation on information or technology from professors or researchers within a short time on such issues a faulty production lines or corporate organization reshuffling etc.
▶ Faculty of Seoul National University must sign any consulting contract through the school before providing a corporation with consulting services, and the consulting contract must include consulting period, consulting method, compensation for consultation, owner ship of intellectual property arising during the consultation process
Joint Research
▶ Also called "Academic-Industrial Cooperation Research," refers to cases where the corporation provides the research expenses and requests the university to develop the necessary technology
▶ Seoul National University uses a standard research agreement which regulates the various issues that may arise during the process of joint research (such as ownership of intellectual property, indemnity of warrantee etc.); therefore any joint research agreements should reflect the standard research agreement as much as possible.
(TIP) As there may be argument regarding intellectual property ownership of an outstanding technology developed during the course of joint research articles regarding intellectual property within the research agreement must be reviewed beforehand by the Intellectual Property Management Headquarters.
Types of Technology Licensing
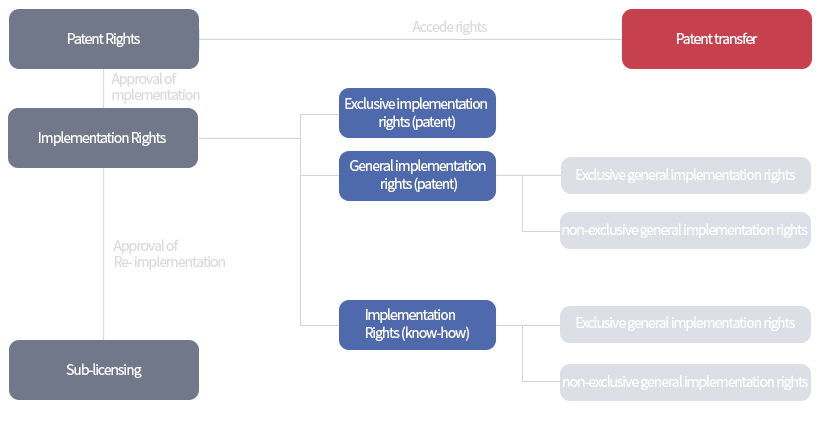
| ·Technology (patent) Transfer - Transferring the ownership rights of a technology to a corporation - As argument may arise in case further research is necessary, to be used only in special cases ·Exclusive implementation rights (or Exclusive implementation rights) - Authorizing only a certain corporation to use the technology (or patent) - More than half of all technology transfer contracts include exclusive implementation right ·General implementation rights - Authorizing several corporation use the technology (or patent) - Used for technological licensing for areas such as where there are several corporations with demand for the technology |
(TIP) Although corporations prefer to receive exclusive implementation rights which enables exclusive use of the technology, universities are careful to prevent cases where the corporation does not make actual use of the technology rights, in which case there are no tangible benefits, through adjusting the payment method for technology or other agreement clauses.
Subjects for Technology Transfer
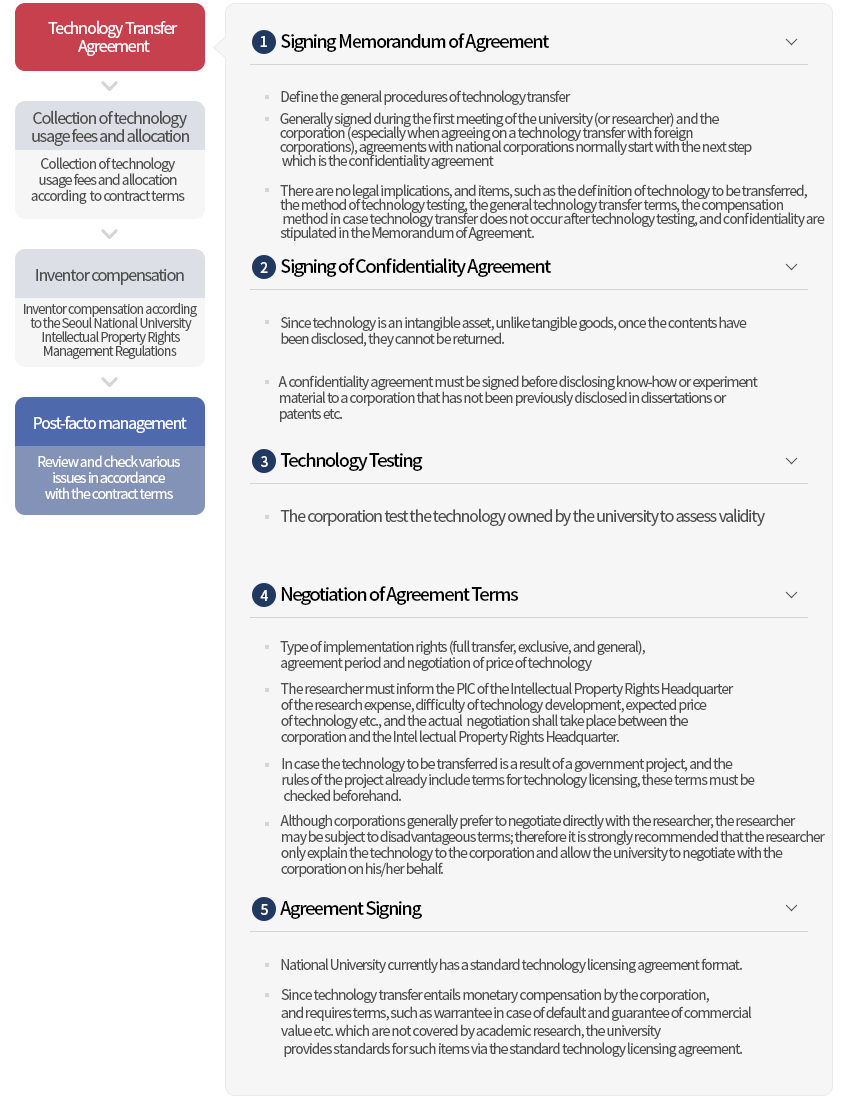
Procedure of Technology Transfer
Person-in-charge: Expert of each field
| Name | Field | Contact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Ji Young
|
Medicine, Pharmacy, Bio: College of Medicine(BT), College of Veterinary medicine(BT), College of Nursing(BT), Graduate school of Public Health, College of Natural Sciences (Bio-sciences, Earth Environment), College of Human Ecology, Graduate school of convergence science and technology(Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences), Center for Food and Bioconvergence |
+82-2-880-2038 | |
| 2 |
Han Yong |
Material, Chemical: College of Engineering(Material Engineering, Chemical and Biological Engineering, Energy Resources Engineering, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Architecture & Architectural Engineering, Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering), College of Education |
+82-2-880-2038 | |
| 3 |
Jung Min |
Electrical, Computer: College of Engineering(Electrical and Computer Engineering, Computer Science and Engineering, Industrial Engineering), Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology(Intelligence Information Convergence), Graduate School of Data Science, Artificial Intelligence Institute |
+82-2-880-2026 | |
| 4 |
Sun Jang |
Medicine, Pharmacy, Bio, Agriculture and Life Sciences: College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, College of Pharmacy, College of Dentistry, College of Natural Sciences(Chemistry) |
+82-2-880-2038 | |
| 5 |
Chae Eun |
Mechanical Engineering, Biomedical Engineering : College of Engineering(Mechanical Engineering, Aerospace Engineering), College of Medicine(IT), College of Veterinary medicine(IT), College of Dentistry(IT), College of Nursing(IT), College of Natural Sciences(Mathematical Sciences, Statistics, Physics & Astronomy, Brain & Cognitive Sciences), Graduate school of Convergence Science and Technology(Applied BioEngineering), Graduate school of Environmental Studies, College of Humanities, College of Social Sciences |
+82-2-880-2026 |
Transferrable Technology
▶ Technology owned by the university with commercial potential or patents with the potential for building a patent portfolio are permanently announced
Distribution of Royalty Revenue
Inventor Compensation
In case of technology fee income due to a technology licensing contract arises, a significant amount of the technology fee is allocated to the inventor in accordance with government project regulations and the 「Seoul National University Royalty Distribution Guidelines」
1. Royalty to be allocated according the implementation of results of government project
| Distribution method of royalty revenue | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Order | First distribution | Remaining technology fees after first distribution | |||
| Agent | Inventor | Expense for applying intellectual property rights and Technology commercialization |
Technology transferor incentive | Inventor | University (SNU R&DB Foundation) |
| Allocation | 50% | 15% or more | 10% | 2/5 | 3/5 |
▶ After the first allocation, 2/5 will be additionally allocated to the inventor, and 3/5 will be allocated to the university.
2. Royalty other than government projects
| Distribution method of royalty revenue | |||||||||
| Section | ~20 million KRW | 20 million ~ 100 milloin KRW |
100 million ~ 500 million KRW |
500 million ~ |
Remarks | ||||
| Agent | Inventor | University (SNU R&DB Foundation) |
Inventor | University (SNU R&DB Foundation) |
Inventor | University (SNU R&DB Foundation) |
Inventor | University (SNU R&DB Foundation) |
|
| Allocation | 100% | 0% | 80% | 20% | 70% | 30% | 50% | 50% | Expense for applying intellectual property rights and expenses related to technology transter to be excluded |



