Professor Byoungyoung Lee's Team at Seoul National University Discovers Security Vulnerability in ARM CPUs Used in Android Smartphones Such as Google Pixel Phones, Increasing Hacking Risks
- Proves the necessity of a solution to smartphone memory protection issues
- Research paper presented at global cybersecurity conference ‘BlackHat USA’

▲ (From left) First author Joohee Kim, corresponding author Professor Byoungyoung Lee
The College of Engineering at Seoul National University has announced that a research team led by Professor Byoungyoung Lee from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering has discovered a security vulnerability in the Memory Tagging Extensions (MTE) feature embedded in CPUs designed by the British semiconductor design company ARM.
This research, conducted jointly by the Systems and Software Security Laboratory at Seoul National University's Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Samsung Research, was presented as a paper titled "Bypassing ARM's Memory Tagging Extension with a Side-Channel Attack" at the global cybersecurity conference 'BlackHat USA 2024' held in Las Vegas, USA, on August 9, 2024. The paper was also published in July on the preprint site arXiv, and a video covering the paper on the international YouTube channel "Low Level Learning," known for its in-depth computer and programming education content, has garnered over 500,000 views, drawing attention within the industry.

▲ Video introducing the research paper on the international YouTube channel ‘Low Level Learning’
The MTE feature, which was introduced by ARM in 2018, is built into the hardware of many Android smartphones, including Google's Pixel 8 and Pixel 8 Pro, as a security measure. Its primary function is to detect memory safety violations and protect devices from bugs that exploit memory vulnerabilities, playing a crucial role in maintaining smartphone security.
The research team discovered that MTE is vulnerable to speculative execution attacks similar to Spectre and Meltdown. Speculative execution attacks exploit a CPU’s technique of predicting program paths to preemptively execute instructions for performance improvement. If the program takes a different path, the results are discarded, but the process exposes security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
The research team also developed a technique to bypass MTE's security detection and used it to extract the MTE tags of specific memory addresses with a success rate of over 95% within 4 seconds, thereby proving a vulnerability in the Android kernel. If MTE’s security protecting the Chrome browser and Linux kernel is compromised, it exposes the system to potential hacking risks.
Professor Byoungyoung Lee, who led the research, commented, "Most Android smartphones have the Chrome browser and Linux kernel installed, so it is crucial to address the security vulnerability in MTE that directly affects smartphone memory security. ARM has acknowledged our team's findings and mentioned them in their developer notes, and Google’s Android security team has awarded our team a bug bounty and is working to resolve the security vulnerabilities in the Pixel 8 device. This recognition demonstrates the significance of our research.“
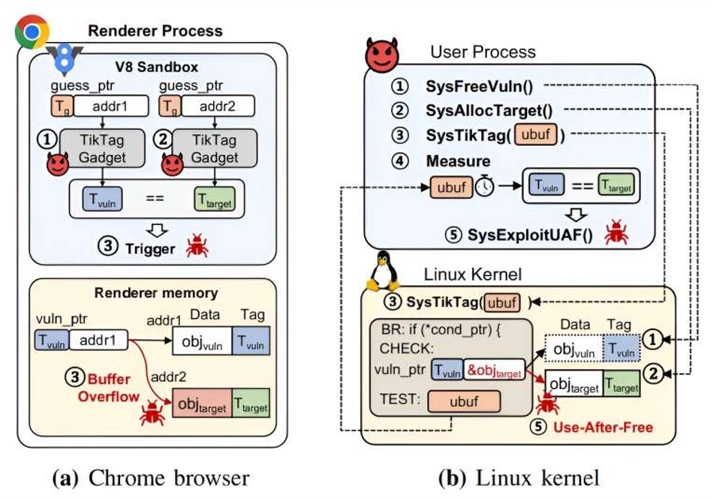
▲ Mechanism of how Chrome and the Linux kernel are attacked due to the security vulnerability in ARM MTE
Meanwhile, the future careers and unique backgrounds of the graduate students from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering who participated in this research as part of the Systems and Software Security Laboratory have garnered significant attention within academic circles.
The first author of the paper, Juhee Kim, has conducted extensive research on ARM MTE attacks and defenses. During this research project, she actively communicated with Google engineers responsible for Chrome, Android, and the Linux kernel, playing a key role in sharing verified research findings with Google.
Co-author Jaeyoung Chung, who has served as the president of Seoul National University's hacking club Guardian, has led activities related to cybersecurity and hacking among undergraduate students. He also advanced to the finals of the DEFCON CTF 32 global hacking competition held in Las Vegas from August 9 to 11, 2024.
Co-author Youngjoo Lee is a unique case of a student who entered the graduate program at Seoul National University’s Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering after obtaining a bachelor's degree through Korea’s Academic Credit Bank System without attending a traditional university. From his high school days, he demonstrated exceptional hacking skills, reporting vulnerabilities in well-known open-source projects and advancing to the finals of DEFCON multiple times. Earlier this year, he conducted visiting research at Professor Xinyu Xing’s laboratory at Northwestern University in the U.S. and is currently participating as a member of a team that advanced to the semifinals of the U.S. Department of Defense’s 'AI Cyber Challenge (AIxCC).‘
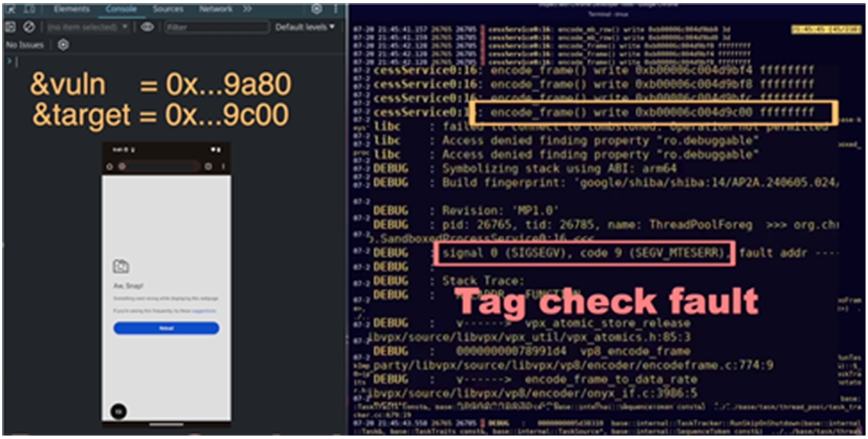
▲ Screen 1 showing the process of an attack exploiting the security vulnerability in the ARM CPU
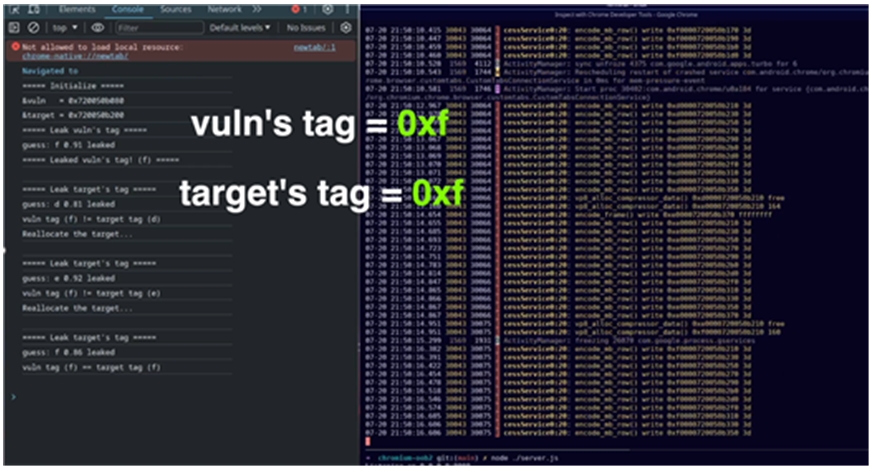
▲ Screen 2 showing the process of an attack exploiting the security vulnerability in the ARM CPU
[Contact Information]
Professor Byoungyoung Lee
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University
Phone: +82-2-880-7266
Email: byoungyoung@snu.ac.kr



